Our law firm provides
international expertise
and a global network.
GGV stands for outstanding expertise,
strategy-focused advice and a strong sense of commitment.
strategy-focused advice and a strong sense of commitment.
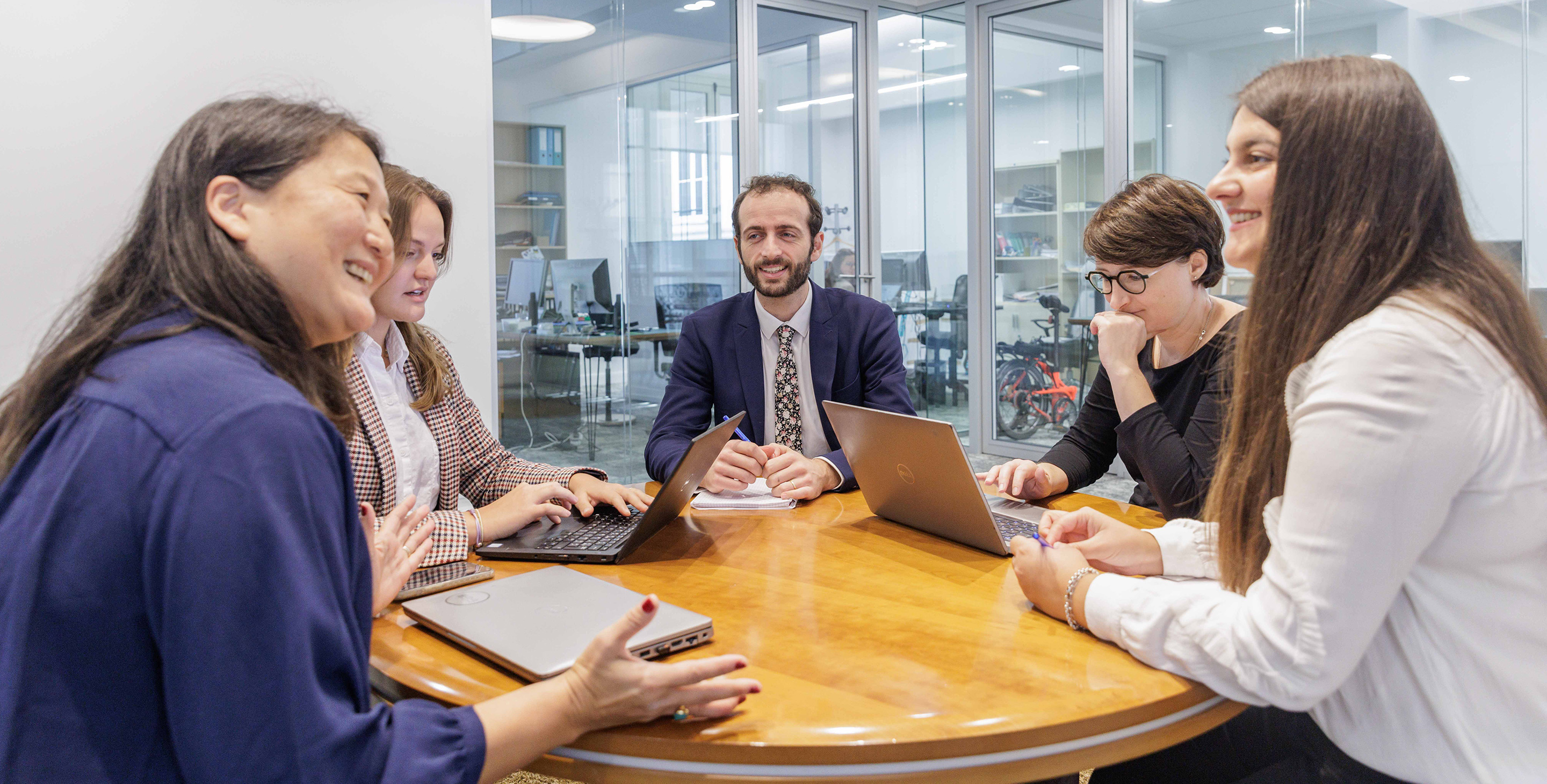

A holistic approach

CSR approach

A strong sense of commitment

A human-scale law firm

International know-how

A holistic approach

CSR approach

A strong sense of commitment

A human-scale law firm

International know-how

A holistic approach
50 Years
Founded in 1974
25
A team of 25 trilingual experts
10
Areas of expertise Multispecialised
and trilingual experts
GGV stands for outstanding expertise,
strategy-focused advice
and a strong sense of commitment.
strategy-focused advice
and a strong sense of commitment.








LATEST NEWS